
 Professional services are guaranteed
Professional services are guaranteed One on one full process guidance
One on one full process guidance Efficient and fast experience
Efficient and fast experience1. Background and positioning
ISO/IEC 29151:2016, also known as "Information Technology - Security Techniques - Practice Guidelines for Personal Information Protection", is jointly published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). This standard is based on the ISO/IEC 27002 (Guidelines for Information Security Control Practices) framework and has been specifically extended and optimized to meet the needs of personal information protection. Its aim is to assist organizations in establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continuously improving their Personal Information Protection Management Systems (PIMS).
2. Scope of application
This standard applies to all entities involved in the collection, storage, processing, or transmission of PII, including but not limited to:
Internet service providers (such as social media platforms);
Financial institutions (payment, credit business);
Medical and health service providers;
Government departments and third-party service providers.
ISO/IEC 29151 proposes a complete system consisting of 35 control objectives and 114 specific control measures, covering three dimensions: governance, technology, and processes. The following is the analysis of the core module:
1. Governance and Risk Management
? PII governance framework
Require organizations to clarify privacy protection policies, define role responsibilities (such as DPO), establish cross departmental privacy governance committees, and ensure high-level commitment to PII protection.
? Risk assessment and disposal
Based on ISO 27005 risk management methodology, identify potential threats in PII processing (such as data breaches, unauthorized access), assess impact levels, and develop risk mitigation plans (such as risk acceptance, transfer, or mitigation).
2. Technical control measures
? Encryption and anonymization
Implement strong encryption (such as AES-256) for PII in storage and transmission, using data anonymization and pseudonymization techniques to minimize recognizability risks.
? Access Control and Audit
Set access policies based on the principle of minimum privilege, implement multi factor authentication (MFA) and dynamic privilege management, and record all PII operation logs for audit tracking.
? System and Network Security
Prevent unauthorized data leakage through technologies such as DLP (Data Leak Prevention) and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), and conduct regular penetration testing and vulnerability repairs.
3. Whole life cycle management
? Collection and Consent Management
Ensure the legality of PII collection, clearly inform users of the purpose of the data, obtain valid consent (such as through dynamic opt in mechanisms), and provide convenient withdrawal channels.
? Data retention and destruction
Develop data retention policies, define storage periods for different categories of PII, and use physical destruction or irreversible encryption erasure techniques to ensure that data is unrecoverable.
4. Compliance and External Responsibilities
? Third party supplier management
Conduct due diligence on data processing partners, bind their security obligations through contracts, and regularly audit their compliance.
? Cross border data transmission
Comply with privacy regulations in the target region (such as EU SCCs and China's Personal Information Export Standard Contract), and implement localized data storage if necessary.
5. Event response and continuous improvement
? Data breach response
Establish a 72 hour emergency response mechanism, clarify the incident reporting process, root cause analysis, and user notification strategy, and regularly practice the effectiveness of contingency plans.
? Continuous improvement mechanism
By conducting internal audits, management reviews, and optimizing the PDCA cycle system, combined with emerging technologies such as privacy enhancing technologies (PETs), we aim to enhance the level of protection.
1. Compliance assurance
Global regulatory adaptation: covering core requirements such as the EU GDPR, China's Personal Information Protection Law, and the US CCPA, reducing the risk of fines for violations (such as GDPR's maximum penalty of 4% of global revenue).
Technical compliance implementation: Clarify mandatory technical measures such as data encryption, access control, and log auditing to ensure compliance with underlying security requirements of privacy regulations.
2. Trust building and brand appreciation
Enhance customer confidence: Through authoritative certifications such as BSI and T ü V, prove to users the ability to protect privacy and reduce customer churn caused by privacy concerns.
Enhancing market competitiveness: In the data-driven industry, compliance and privacy capabilities have become differentiated advantages, helping enterprises obtain more cooperation opportunities.
3. Systemic risk management
Reduce the risk of data breaches: Through techniques such as Privacy Impact Assessment (PIA) and data minimization, the average occurrence rate of data breaches has been reduced by 37% (ISO statistics).
Rapid response capability: Establish a 72 hour data breach emergency mechanism to reduce the impact of the incident and repair costs (referring to the average cost of $4.45 million for IBM data breaches).
4. Optimize resource allocation
Avoid redundant construction: Integrate information security management requirements such as ISO 27001 to reduce redundant investment.
Precise risk prevention and control: Through continuous monitoring and PDCA improvement, optimize security resource allocation, and focus on high-risk scenarios (such as third-party management and cloud environment protection).
5. Strategic and Cultural Values
Embedding privacy protection culture: By providing employee training and standardizing processes, we aim to enhance privacy awareness among all employees and establish an organizational culture of proactive protection.
Support business innovation: The principle of Privacy by Design helps new products/services to quickly land within a compliant framework, balancing data value mining with user rights.
ISO/IEC 29151 is a practice guide standard that does not provide direct certification, but organizations can establish a Personal Information Protection Management System (PIMS) based on its requirements and conduct compliance assessments through third-party organizations. The following are the core points of application requirements and materials:
(I.) Application materials
If compliance assessment or certification needs to be conducted through a third-party organization, the following materials must be prepared:
1. System documents
Privacy Policy and Objectives: Clarify management commitments and compliance objectives for personal information protection.
Scope statement: Define the business scope, data types, and processing scenarios covered by the system.
Risk assessment report: including risk analysis and control measures for personal information processing activities.
Control measures document: Implementation plan for control items required by ISO/IEC 29151, such as encryption policies and access control rules.
Training Record: Employee Privacy Awareness Training and Job Responsibilities Explanation.
Internal audit and management review report: a record that proves the effectiveness of the system's operation.
2. Legal Compliance Certificate
Cross border data transfer protocols (such as SCCs, BCRs), privacy statements, user consent records, etc.
3. Supplementary materials for third-party certification
Certification application contract: an audit agreement signed with the certification body.
On site audit support materials:
Record of data processing procedures (such as data collection forms, storage location lists);
Technical control evidence (such as encryption configuration screenshots, access logs, monitoring system reports);
Event response records (such as data breach drill reports, emergency notification processes).
(II.) Application requirements
1. System foundation
An Information Security Management System (ISMS) has been established, and it is recommended to base it on the ISO/IEC 27001 standard (as 29151 is an extension of 27002).
Having a management process for the entire lifecycle of personal information, including collection, storage, processing, transmission, and destruction.
2. Implementation of control measures
35 control measures specified in ISO/IEC 29151 have been implemented, including encryption, access control, data classification, and protection of user rights.
Complete privacy risk assessment and develop a risk mitigation plan.
3. Internal Audit and Improvement
Verify the effectiveness of the system through internal audits and conduct management reviews to ensure continuous improvement.
4. Compliance requirements
Ensure compliance with applicable privacy regulations (such as GDPR, CCPA, China's Personal Information Protection Law, etc.).

Through the above process, organizations can effectively establish and maintain a personal identity information protection management system, enhance privacy protection capabilities, meet regulatory requirements, and strengthen customer trust




Wechat ID:Siterui888888
Add a wechat friend to get free plans and quotations
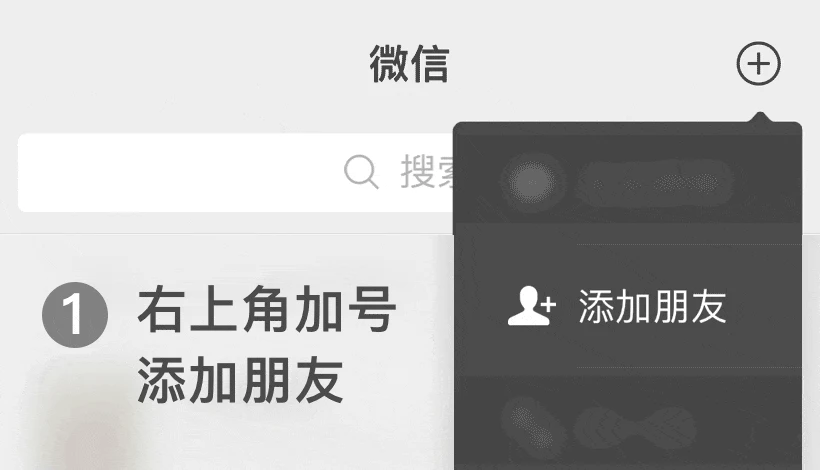

 Contact
Contact
號(hào).jpg)

 定制化解決方案
定制化解決方案 專業(yè)咨詢指導(dǎo)
專業(yè)咨詢指導(dǎo) 透明化服務(wù)
透明化服務(wù) 長期顧問式合作
長期顧問式合作