7D1AC8FA46A9412C9FBE991B76C879F6.jpg)
 Professional services are guaranteed
Professional services are guaranteed One on one full process guidance
One on one full process guidance Efficient and fast experience
Efficient and fast experienceISO 22301 is the world's first authoritative standard for Business Continuity Management (BCM) published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). This standard provides a systematic methodology for enterprises to ensure that critical business functions can continue to operate or be restored in the shortest possible time in the face of emergencies such as natural disasters, cyber attacks, supply chain disruptions, etc., minimizing economic losses, maintaining customer trust, and safeguarding organizational reputation. It goes beyond traditional disaster recovery concepts and provides a complete, process based management system standard.
Its core goal is to assist organizations in:
1. Identify potential threats: Systematically identify internal and external threats that may have a significant impact on organizational operations (natural disasters, accidents, human sabotage, technological failures, supply chain disruptions, etc.).
2. Evaluate business impact: Analyze the financial, reputational, compliance, and operational impacts of interruption events on critical business processes, activities, and resources (personnel, technology, location, information), and determine recovery priorities (RTO, RPO).
3. Establish effective response capability: Develop, implement, and maintain a written Business Continuity Plan (BCP) and specific business continuity strategies to ensure rapid recovery in the event of an interruption.
4. Building organizational resilience: Through continuous improvement, enhance the overall ability of the organization to prevent, resist, respond to interruptions, and recover from their impact, ensuring the continuous delivery of key products/services to stakeholders.
The ISO 22301 Business Continuity Management System adopts the PDCA (Plan Do Check Improve) process approach, which identifies, analyzes, and alerts risks to help businesses avoid potential events and quickly recover from interruptions, minimizing losses and recovery costs.
The core content of BCMS includes the following aspects:
1. Business Impact Analysis (BIA): Determine the priority, recovery sequence, and indicators of products or services by evaluating the degree of impact caused by interruptions in the organization's product or service activities. This is one of the core processes of BCMS, involving multiple steps such as defining business scope, data collection and analysis, analyzing business importance, and resource analysis.
2. Risk assessment and management: Identify potential threats, assess the impact of these threats on the normal operation of the enterprise, and determine the corresponding risk level. Organizations need to develop strategies to mitigate, transfer, or accept these risks, such as by backing up data, establishing disaster recovery plans, or forming emergency response teams.
3. Business Continuity Plan (BCP): Develop a detailed plan to guide an organization in responding, recovering, restarting, and restoring to a predetermined level of business operations in the event of a business interruption. The plan needs to cover key indicators such as critical business processes, resource requirements, recovery time objectives (RTO), and recovery point objectives (RPO).
4. Clear organizational structure and responsibilities: Establish a clear organizational structure, clarify the responsibilities and authorities of each department in business continuity management, and ensure efficient organizational response in case of emergencies.
ISO 22301 applies to all types of organizations, regardless of their size, industry, or business nature. From information security, information technology services, public services, social organizations, to high-risk industries such as business, finance, and manufacturing, implementing ISO 22301 can enhance one's ability to resist risks.
Implementing ISO 22301 business continuity management system can bring many significant advantages to organizations:
1. Enhance organizational resilience and survival capability:
Significantly reduce the impact of interruption events on core business operations, ensure the survival and rapid recovery of the organization in crisis, and maintain market position.
2. Protecting reputation and brand value:
Demonstrate professional and responsible response capabilities during crises, maintain the trust of key stakeholders such as customers, investors, and regulatory agencies, and minimize reputational damage.
3. Meet compliance and contractual requirements:
More and more regulations (such as in finance, healthcare, and critical infrastructure sectors) and large customer contracts require organizations to demonstrate effective business continuity capabilities. ISO22301 certification is the strongest evidence of compliance.
4. Reduce financial losses and insurance costs:
Reduce direct income losses, contract penalties, and additional cost expenditures caused by interruptions. Some insurance companies may offer more favorable premiums to certified organizations.
5. Enhance competitive advantage and customer confidence:
Showcasing the organization's strong risk management capabilities and commitment to service continuity to the market becomes a key differentiation advantage, enhancing the confidence of customers and partners.
6. Optimize decision-making and resource allocation:
The BIA process forces organizations to gain a deep understanding of their key businesses and dependencies, providing critical insights for strategic decision-making and resource optimization.
7. Improve internal collaboration and awareness:
Cross departmental participation in BCMS construction, clarifying roles and responsibilities, enhancing risk awareness and emergency response capabilities of all staff, and strengthening organizational cohesion.
(I.) Application materials
1. Legal status proof documents: such as the business license of the enterprise legal person, the code certificate of the public institution legal person, the registration certificate of the association legal person, etc., and a copy of the organization code certificate stamped with the official seal. When there is a branch office, copies of the branch office's business license and organizational code certificate with official seal should be submitted.
2. Temporary site list: such as the list of construction projects under construction, information security management system, and temporary service points for information technology service management system.
3. List of applicable laws, regulations, and standards.
4. Administrative licensing documents: Obtain the administrative licensing documents required by relevant laws and regulations (when applicable).
5. Business Impact Analysis Report, Risk Assessment Report, and Business Continuity Plan.
6. BCMS system documents: including policies, objectives, scope, and information maintained by the organization for process operation and communication. It is necessary to provide an organizational profile, organizational structure (organizational chart), personnel situation and functional division, process roadmap/process flow chart/process description (which should clearly indicate key and special processes) and related process documents.
(II.) Application requirements
1. Legal and valid proof of legal status: The applying organization should hold a legal entity business license or a document proving its legal status.
2. Risk identification and assessment: Risks have been fully identified and assessed for their impact on the business.
3. System operation time: The operation time of the business continuity management system shall not be less than 3 months, and some institutions require 6 months.
4. Internal audit and management review: Complete at least one internal audit and management review.
5. Resource allocation: Enterprises are equipped with corresponding personnel, equipment and facilities, office/operating conditions, etc.
The following is a standardized flowchart based on the entire ISO 22301 certification process:




Wechat ID:Siterui888888
Add a wechat friend to get free plans and quotations
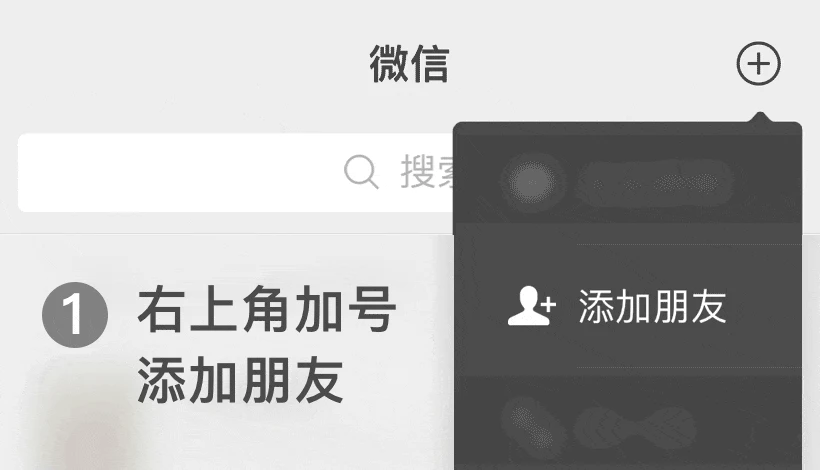

 Contact
Contact
號.jpg)

 定制化解決方案
定制化解決方案 專業(yè)咨詢指導(dǎo)
專業(yè)咨詢指導(dǎo) 透明化服務(wù)
透明化服務(wù) 長期顧問式合作
長期顧問式合作