
 Professional services are guaranteed
Professional services are guaranteed One on one full process guidance
One on one full process guidance Efficient and fast experience
Efficient and fast experienceThe core concept of HACCP is to reduce food safety risks to an acceptable level through scientific analysis and monitoring of critical processes, rather than relying on traditional post inspection methods. The HACCP system has been internationally recognized as an effective tool for ensuring food safety and is widely used in food production, processing, storage, transportation, and catering services.
Historical background and development
Origin: In the 1960s, NASA collaborated with Pillsbury to develop aerospace food products to ensure zero defect food safety standards.
International recognition: In 1993, the Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC) officially incorporated HACCP into the General Principles of Food Hygiene, becoming a universal guideline for the global food industry.
Regulatory requirements: Major economies such as the European Union, the United States, and China have listed HACCP as a mandatory regulatory requirement for food enterprises (such as EU EC 852/2004 and China GB/T 27331)
1. Hazard Analysis
Comprehensive identification and risk assessment of potential biological (such as pathogenic bacteria), chemical (such as pesticide residues), and physical (such as metal foreign objects) hazards throughout the entire food production process (from raw materials to consumption). For example, in rice production, attention should be paid to the production environment, pesticide use, and processing pollution.
2. Determine Key Control Points (CCPs)
Determine the steps that have a decisive impact on food safety through analysis. For example, the ozone dosing process in water plants needs to control the risk of bromate generation, while high-temperature sterilization is a key control point in meat processing.
3. Establish Critical Limits
Set quantifiable safety thresholds for each CCP. For example, the amount of ozone added should be controlled at 0.07-0.10 mg/L to avoid excessive by-products.
4. Monitoring program
Real time monitoring of the operating status of CCPs through online detection (such as temperature sensors) or offline sampling (such as microbiological testing) to ensure compliance with limit requirements.
5. Corrective Actions
When deviations are detected during monitoring, immediate corrective measures should be taken, such as suspending production, adjusting processes, or destroying problematic products, and tracing the root cause to prevent recurrence.
6. Verification program
Regularly review the effectiveness of the HACCP plan, including document review, on-site inspection, and third-party certification, to ensure continuous improvement of the system.
7. Documentation and Traceability
Complete preservation of production records, monitoring data, and correction reports, achieving full traceability throughout the process. For example, water plants need to record ozone dosing parameters and water quality testing results.
The HACCP system applies to all links in the food chain that may affect food safety, mainly covering the following areas:
1. Food production and processing
Manufacturing industry: dairy products, meat products, aquatic products, beverages, canned goods, baked goods, etc.
Key processes: risk control in sterilization, freezing, packaging, metal detection, and other stages.
2. Catering Services and Retail
Catering industry: central kitchen, chain restaurants, school and enterprise canteens.
Retail industry: Food storage and sales management in supermarkets and fresh food e-commerce.
3. Supply chain management
Raw material procurement: Quality and safety verification of agricultural products and additives.
Logistics process: cold chain transportation, storage temperature and humidity control.
4. Special food field
Products with high safety requirements such as infant formula, health food, and aerospace food.
The application advantages of HACCP system are significant, mainly reflected in the following aspects:
1. Prevention first
The HACCP system emphasizes the prevention of hazards rather than relying on inspection of the final product. By setting key control points and conducting strict monitoring during the production process, potential problems can be identified in a timely manner and corrective measures can be taken, effectively avoiding the occurrence of food safety accidents
2. Reduce risks
This system can systematically identify and evaluate various hazards in the food production process, and reduce risks to an acceptable level through control measures at key control points. Compared with traditional quality control methods, the HACCP system is more scientific and effective in controlling food safety risks
3. Improve efficiency
The implementation of HACCP system helps food enterprises optimize production processes, allocate resources reasonably, and improve production efficiency. Enterprises can focus their energy on key control points, avoiding comprehensive monitoring of the entire production process, thereby reducing production costs
4. Enhance the competitiveness of enterprises
Today, as food safety is increasingly valued, companies with HACCP system certification are more competitive in the market. This not only helps to enhance the brand image of the enterprise and increase consumer trust in the product, but also provides strong support for the enterprise to explore domestic and international markets
(I.) HACCP certification application materials
Enterprises need to submit the following core materials to the certification body (specific requirements shall prevail):
1. Enterprise qualification documents
Copy of business license, organization code certificate, and food production license.
Factory floor plan, workshop layout, equipment list, and hygiene permit certificate.
2. HACCP system documents
HACCP plan: including hazard analysis table, CCP judgment basis, critical limits, and monitoring procedures.
Supporting documents:
Process flowchart (requires on-site verification and signature).
Product description (ingredients, packaging, storage conditions, expected use, etc.).
Program files (hygiene control, recall procedures, corrective measures, etc.).
3. System operation records
Monitoring records: CCP point detection data (such as temperature records, metal detection reports).
Correction record: Deviation event handling and correction certificate.
Verification reports: internal audits, management reviews, third-party testing reports, etc.
4. Personnel training certificate
HACCP team member qualification certificate (such as internal auditor training certificate).
All staff food safety and HACCP training records and assessment results.
5. Other materials
Certification application form (stamped with official seal).
List of applicable laws and regulations and compliance statement.
Supplementary documents required by the certification body (such as supplier qualification audit records).
(II.) HACCP certification application conditions
Enterprises need to meet the following basic conditions in order to apply for HACCP certification:
1. Legal business qualifications
Holding valid business license, food production/operation license and other legal qualification documents.
Comply with relevant national and industry regulations (such as the Food Safety Law and GB 14881 General Hygiene Standards for Food Production).
2. HACCP system has been established and operated
Complete the establishment and trial operation of the HACCP system (usually requiring effective operation for more than 3 months).
Have complete system documents (HACCP plan, procedure documents, work instructions, etc.).
3. Infrastructure and resource security
The production environment, equipment, and processes meet the requirements of food safety and hygiene.
Equipped with necessary testing equipment (such as thermometers, metal detectors) and professional personnel.
4. Internal audit and management review
Complete at least one internal audit covering the entire process and keep records.
The top management leads the management review to confirm the continued suitability of the system.
5. No major food safety accidents
There have been no systemic food safety issues or administrative penalties within the year prior to the application.
1. Preparation stage
Team building: Establish cross departmental teams (production, quality, research and development, etc.).
Regulatory research: Clarify applicable standards (such as GB 27331, ISO 22000).
Resource preparation: equipped with testing equipment, training budget, and technical support.
2. System establishment
Flowchart drawing: Sort out the entire process steps from raw materials to finished products.
Hazard analysis: Identify biological, chemical, and physical hazards (such as pathogenic bacteria, pesticide residues).
Determine CCP: Screen key control points (such as sterilization, metal detection).
Setting limits and monitoring: Clarify key limits (such as temperature/time) and monitoring methods.
3. Trial operation and verification
Internal audit: Test the effectiveness of CCP and simulate corrective scenarios.
Third party certification: audited by certification bodies such as SGS and Intertek.
4. Operation and maintenance
Daily monitoring: Record CCP data (temperature, detection results).
Regular review: Conduct at least one management review annually to update the HACCP plan.
Continuous improvement: Optimize system vulnerabilities through CAPA measures.




Wechat ID:Siterui888888
Add a wechat friend to get free plans and quotations
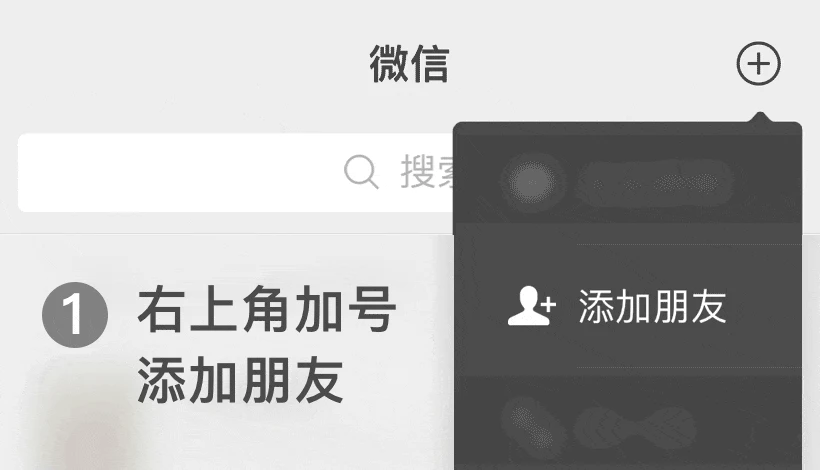

 Contact
Contact
號.jpg)

 定制化解決方案
定制化解決方案 專業(yè)咨詢指導(dǎo)
專業(yè)咨詢指導(dǎo) 透明化服務(wù)
透明化服務(wù) 長期顧問式合作
長期顧問式合作